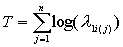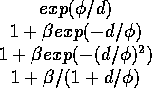Bithell's Linear Risk Score Test
|
|
|
|
Indications/Recommendations for use: Detects excess risk near a point source. A relative risk function specifies a pattern of risk corresponding to the alternative hypothesis under consideration.
|
|
Description: Each case is assigned a risk score given by the
logarithm of the relative risk for their region.
(More)
|
|
Test statistic: The sum of the risk scores provides the test statistic.
|
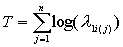
|
Null Hypothesis:
The case counts in the regions are independently,
Poisson distributed with means equal to the appropriate region-specific relative risk
multiplied by the regional expected case counts.
|
Ho: The parameters in the functions below are such that the RRF=1.
|
|
Alternative Hypothesis:
Each case is assigned a risk score given by the logarithm of the relative
risk function for their region. GeoMed supports four relative risk
functions at right.
|
| Ha: RRF is |
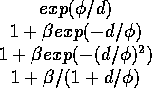 |
|
|
GeoMed Inputs:
Region-level data with centroid coordinate, case counts, and population-at-risk per region; point-focus coordinate.
|
|
GeoMed Outputs:
Test statistic and p-value; 2-D plot of smooth relative risk function and observed, region-specific relative risks.
|
|
Example Analysis
|
Reference:
Bithell, J.F. 1995. The choice of test for detecting raised disease risk near a point source. Stat Med, 14:2309-2322.
|