Make a list of all definitions in the section (a few words each is fine). Summarize any lengthy definitions introduced in this section in your own words.
-
second derivative: the derivative of the derivative of f is called the
second derivative of f, denoted
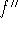 .
.
In the context of the position function of a particle, the second derivative of the position is known as the acceleration of the particle.
-
third derivative: the derivative of the second derivative of f is
called the third derivative of f, denoted
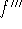 .
.
In the context of the position function of a particle, the third derivative of the position is known as the jerk.
-
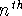 derivative: if we differentiate a function n times, we obtain
the
derivative: if we differentiate a function n times, we obtain
the 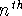 derivative (which doesn't necessarily have a nice intuitive
sense). It will be denoted
derivative (which doesn't necessarily have a nice intuitive
sense). It will be denoted

-
n factorial: the product of all positive integers less than or equal
to n.
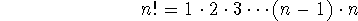
Make a list of all theorems (lemmas, corollaries) in the section (a few words each is fine). Summarize each one introduced in this section in your own words.
none that I noted.
Make a note of any especially useful properties, tricks, hints, or other materials.
The best interpretation of the second and third derivatives comes in the context of the position function s(t) of a particle. Then the velocity is the first derivative of s, while the acceleration of the particle is the first derivative of the velocity, and the second derivative of the position.
![]()
The third derivative is the derivative of the acceleration, and is perhaps best known as the jerk.
Summarize the section in two or three sentences.
This section introduces the concept of higher derivatives, and in particular the second and third derivatives. The second derivative is just the derivative of the derivative, so everything we've learned about derivatives applies to it. The same is true for higher derivatives, although they just get farther removed from the original function f in general.
You should pay special attention to the graphical relationship between
successive derivatives. For example, ![]() when the function
when the function
![]() has a horizontal slope. Knowing things about higher derivatives
gives us more information about the shape of f (as the roots of the
derivative function indicate points of horizonal slope on the graph of f).
has a horizontal slope. Knowing things about higher derivatives
gives us more information about the shape of f (as the roots of the
derivative function indicate points of horizonal slope on the graph of f).