![]()
![]()
or
![]()
(expands in terms of x by default). If you want the expansion in terms of a, then you would type
![]()
which would give
![]()
Note:
![]()
![]()
![]()
The coefficients of each term come from Pascal's triangle:
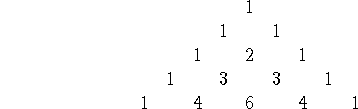
Etc.!
![]()
Factor will try to create linear terms in x (by default), i.e.
![]()
![]()
returns ![]() . I personally prefer to define a function in the ``Y='' menu,
e.g.
. I personally prefer to define a function in the ``Y='' menu,
e.g.
![]()
and then use
![]()
If you have to use a function over and over, it's usually smart to define it in a way that will be stored for future use.
Now we can do things like solve for where the derivative is zero:
![]()
![]()
for example yields ![]() , one of the most important
trig identities.
, one of the most important
trig identities.
![]()
yields another: ![]() .
.
![]()
This command would represent the sum
![]()
which is similar to the type of sum we need when creating Riemann sums.