- Your 6.1 homework is returned: graded 4, 16, and 32.
- Yes and no answers are not sufficient -- you have to give reasons.
- Label graphs. Tick marks, with numerical values.
- Your 6.2 homework is due today.
- Your 6.3 homework is due Monday.
- Our second exam is next Friday, but the Friday next (3/27); it will cover through 6.3.
- This section features the logarithm taking care of some tricky cases that we couldn't handle previously, through a process called "logarithmic differentiation".
Let's see this process in action, on an interesting function: the example 16, p. 417.
- Let's look at the summary section
6.4 for some of the results of this section.
Now I'd like to go over the result following example 16, entitled "The Number e as a Limit". It incorporates some nice elements of limits, including that limit definition.
- Examples:
- #11, p. 418
- #44
- #78
- The first place to start is the geometric perspective, perhaps.
As usual, we're focused on the undoing property: if the question for us begins as "What is sine of 30 degrees?", the undoing question is "Whose sine is
?"
We should immediately observe that the original question has a unique solution, whereas the "undoing question" does not. Because sine is not one-to-one, we shouldn't be surprised. But this is an issue: how do we create a useful "inverse" of a non-invertible function?
- Well, we need to worry in particular about three functions: sine,
cosine, and tangent (the others -- secant, etc. -- I don't really worry
about too much, but they do sometimes come into play: for example, they
provide anti-derivatives for another group of functions -- see p. 457):
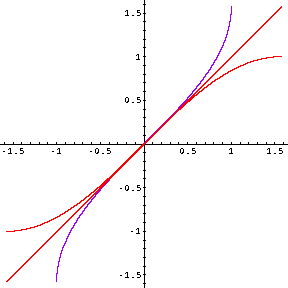
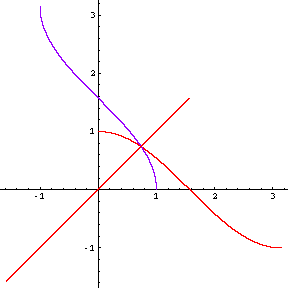
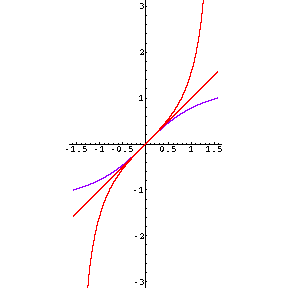
- Two of these inverse functions are shown in their entirety; the other isn't. Which is which?
- What features of a graph would have helped us to identify these more easily?
- One of these also illustrates the fact that a function can increase forever, without tending to infinity -- it asymptotes to a finite value. What is it?
- The graphical definitions of these functions are easy, carried out
via the mirror. But what are the properties of these inverses?
For example, what are their derivatives? These we've carried out before, using the amazing rule for inverse functions -- do you remember it?
Let's try it with arctan...
- Can you relate arcsin and arccos? Can you obtain one from the
other using shifts, reflections, etc.?
- Let's look at a few problems involving these curious inverse
functions:
- 1, p. 459
- 6
- 14
- 18, p. 460
- 22
- 48
- 49