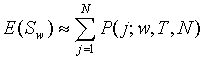
A test for temporal clustering in a single time series.
Data Requirements
Time series of case counts
Window width
Analysis
H0: Cases occur at random across the time series
Ha: Cases cluster in some time periods
Test Statistic: The maximum number of cases appearing in a pre-defined window as it is moved continuously along a time series. When the cases are clustered the maximum number of cases in the scanning window will be large. The expectation under the null hypothesis, E(Sw) is: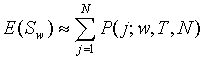
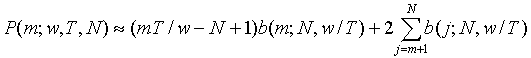
and where N is the total number of cases, T is the number of time periods, w is window width, and Sw is the maximum number of cases observed in w as it is slid along the time series. Sw is larger than its expectation when cases cluster in a few time cells. Sw is smaller than its expectation when cases are uniformly distributed among the time cells. The probability of observing, under the null hypothesis, an Sw given the window width w, T time periods and N cases is approximated by:
Here
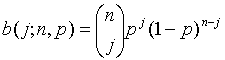
![]() is a binomial coefficient. P(j;w, T, N) is the probability of obtaining, under the null hypothesis, a scan statistic greater than or equal to j. This probability is one-tailed.
is a binomial coefficient. P(j;w, T, N) is the probability of obtaining, under the null hypothesis, a scan statistic greater than or equal to j. This probability is one-tailed.
Output
Total number of cases and the window width
The scan statistic, its expectation, and the p-value
Graph of Sw on its expectation with 45 degree line through origin
Reference
Jacquez, G.M. 1994, User manual for Stat!: Statistical software for the clustering of health events, BioMedware, Ann Arbor, MI.