Knox test
|
|
|
|
Indications/Recommendations for use:
When space-time interaction is present cases near in space will also be near in time, and the
test statistic will be large (more).
|
|
Description:
A test for space-time interaction using critical space and time distances
(provided by the user). Pairs of cases separated by less than the critical
space distance are considered to be near in space. Pairs of cases separated
by less than the critical time distance are said to be near in time.
|
|
Test statistic:
The number of pairs of cases that are near to one another in both space and
time.
|
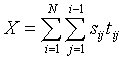
|
|
Null Hypothesis:
Whether cases are near in space is independent of whether they are near in time.
|
Ho: The null distribution of X is constructed under an approximate randomization which permutes the row-column elements of the time adjacency matrix while holding the space adjacencies constant, a number of times specified by the user. The probability value is the proportion of the upper right hand tail of the null distribution whose X values are as large or larger than the test statistic.
|
|
Alternative Hypothesis:
Pairs of cases near in space tend to be near in time.
|
|
GeoMed Inputs:
Space and time distances between pairs of cases, and critical space and time
distances.
|
|
GeoMed Outputs:
|
|
Example Analysis
|
Reference:
Knox, G. 1964. The detection of space-time interactions. Applied
Statistics, 13:25-29.
Knox, G. 1963. Detection of low intensity epidemicity: application to
cleft lip and palate. British Journal of Preventive and Social
Medicine, 18:17-24.
|