Quiz 1 Answer: Because if we pass the expectation through the
sum, and all points ![]() have the same expectation, then we can pull this
common expectation out of the sum to get
have the same expectation, then we can pull this
common expectation out of the sum to get
![]()
and if
![]()
the result follows.
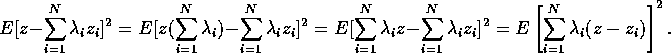
![]()
This follows from the expansion
![]()
![]()
which is solved for ![]() .
.
Quiz 4 Answer: Again, we use the constraint that the sum of the weights is 1:
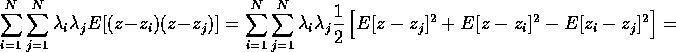
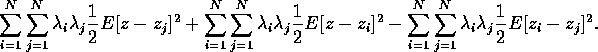
In each of the first two terms we can slip one indexed sum to the outside: e.g.,
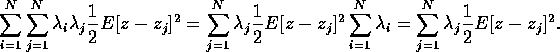
Similarly,
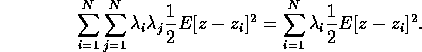
The two sums are seen to be equal, however, as the index is just a dummy (try telling that to the index!). Thus we end up with (4).